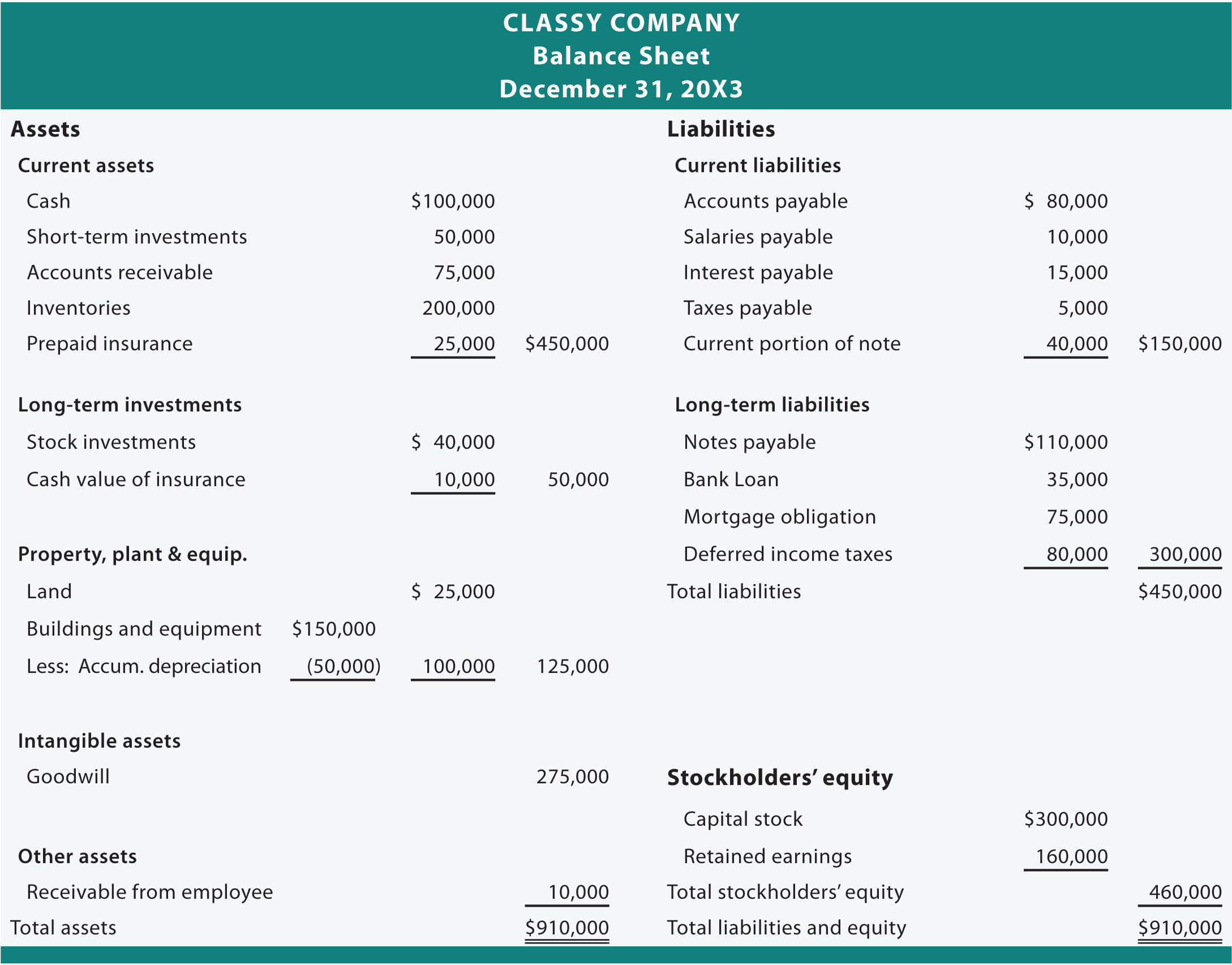
So for the asset side, the accounts are classified typically from most liquid to least liquid. For the liabilities side, the accounts are organized from short- property and equipment definition to long-term borrowings and other obligations. These financial statements can only show the financial metrics of your company at a single moment in time.
Balance sheet equation
By understanding each part of the balance sheet, you can provide the most in-depth analysis. A balance sheet is a financial statement that communicates the “book value” of an organization, as calculated by subtracting all of the company’s liabilities and shareholder equity from its total assets. Financial ratio analysis uses formulas to gain insight into a company and its operations.
Pay your team
As you can see, it starts with current assets, then the noncurrent, and the total of both. Like assets, liabilities can be classified as either current or noncurrent liabilities. Noncurrent assets include tangible assets, such as land, buildings, machinery, and equipment. The revenues of the company in excess of its expenses will go into the shareholder equity account.
Business
A balance sheet represents a company’s financial position for one day at its fiscal year end—for example, the last day of its accounting period, which can differ from our more familiar calendar year. Companies typically select an ending period that corresponds to a time when their business activities have reached the lowest point in their annual cycle, which is referred to as their natural business year. Overall, a balance sheet is an important statement of your company’s financial health, and it’s important to have accurate balance sheets available regularly. Balance sheets are important because they give a picture of your company’s financial standing. Before getting a business loan or meeting with potential investors, a company has to provide an up-to-date balance sheet. A potential investor or loan provider wants to see that the company is able to keep payments on time.
After the first year, your car would be shown on the balance sheet at the purchase price of $40,000 minus $8,000 accumulated depreciation, for a net book value of $32,000. As with assets, these should be both subtotaled and then totaled together. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. The comparative balance sheet presents multiple columns of amounts, and as a result, the heading will be Balance Sheets.
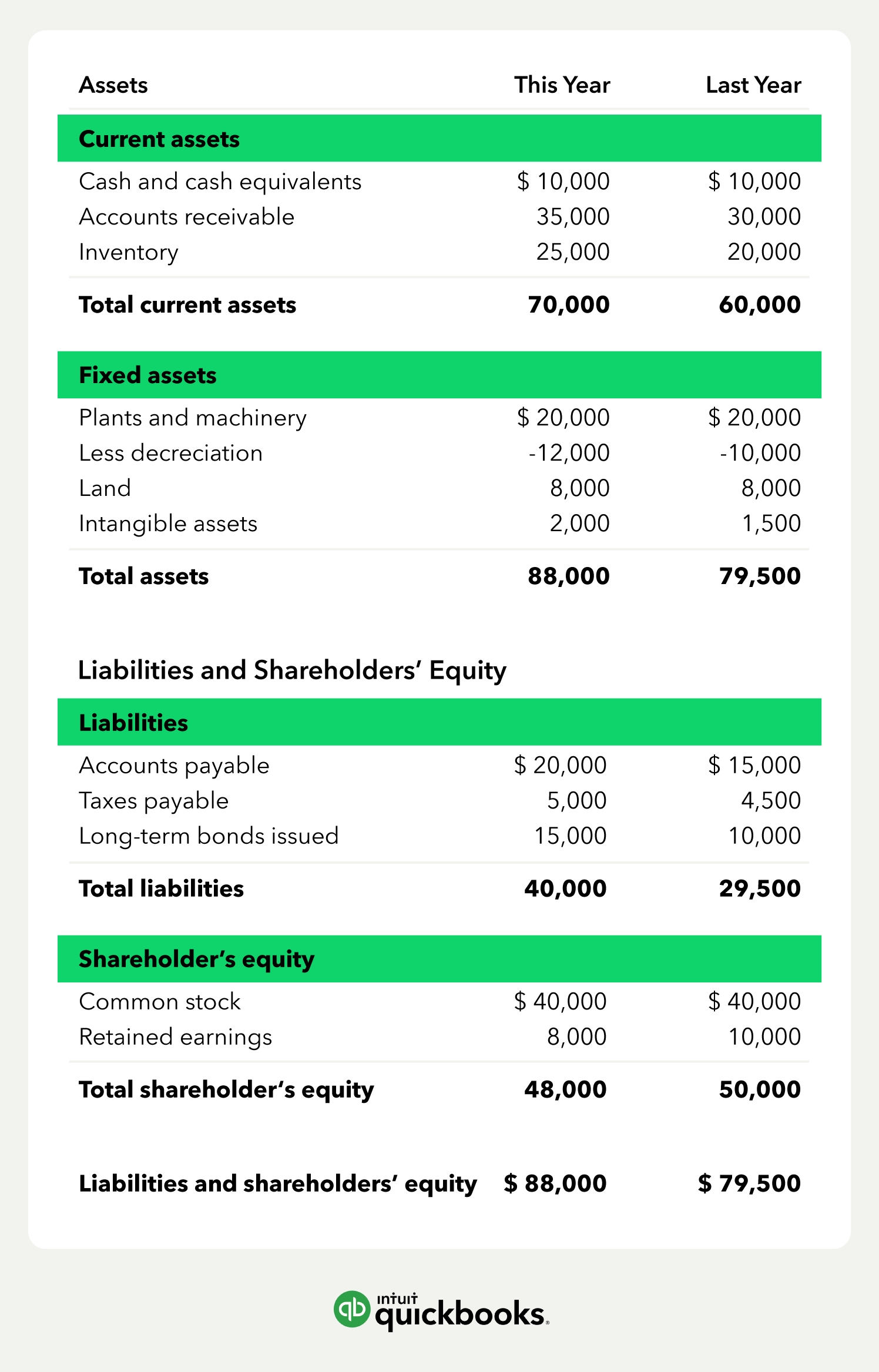
Depending on the company, different parties may be responsible for preparing the balance sheet. For small privately-held businesses, the balance sheet might be prepared by the owner or by a company bookkeeper. For mid-size private firms, they might be prepared internally and then looked over by an external accountant. The image below is an example of a comparative balance sheet of Apple, Inc. This balance sheet compares the financial position of the company as of September 2020 to the financial position of the company from the year prior. Retained earnings are the net earnings a company either reinvests in the business or uses to pay off debt.
This analysis is crucial in assessing short-term financial stability, especially in industries with fluctuating demand cycles. A balance sheet is meant to depict the total assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity of a company on a specific date, typically referred to as the reporting date. Often, the reporting date will be the final day of the accounting period. With this information, stakeholders can also understand the company’s prospects. For instance, the balance sheet can be used as proof of creditworthiness when the company is applying for loans.
- Finally, unless he improves his debt-to-equity ratio, Bill’s brother Garth is the only person who will ever invest in his business.
- Balance sheets organize assets by liquidity or how easily they convert to cash.
- You may have omitted or duplicated assets, liabilities, or equity, or miscalculated your totals.
- Want to learn more about what’s behind the numbers on financial statements?
- The purpose of a balance sheet is to give interested parties an idea of the company’s financial position, in addition to displaying what the company owns and owes.
Assets are typically listed as individual line items and then as total assets in a balance sheet. Investors, creditors, and internal management use the balance sheet to evaluate how the company is growing, financing its operations, and distributing to its owners. It will also show the if the company is funding its operations with profits or debt. Unlike the asset and liability sections, the equity section changes depending on the type of entity. For example, corporations list the common stock, preferred stock, retained earnings, and treasury stock. Partnerships list the members’ capital and sole proprietorships list the owner’s capital.
As you can see, the report form presents the assets at the top of the balance sheet. Beneath the assets are the liabilities followed by stockholders’ equity. In the account form (shown above) its presentation mirrors the accounting equation.
For this reason, a balance alone may not paint the full picture of a company’s financial health. When analyzing a company’s liquidity, the current ratio and quick ratio are essential indicators. If the company’s inventory is 100,000 dollars, the , showing the company’s ability to meet obligations without depending heavily on inventory.
